Definition
Erythrocytes sedimentation rate is the rate at which the
erythrocytes settle down. Normally the red blood cells remain suspended
uniformly in circulation. This is called suspension stability of RBCs. If blood
is mixed with an anticoagulant and allowed to stand on a vertical tube,
the red cells settle down due to gravity with a supernatant layer of clear
plasma. ESR is also called sedimentation rate sed rate or biernacki reaction.
It was firtst demonstrated by Edmund Biernacki in 1897.
DETERMINATION OF ESR
1. WESTERGREN METHOD
2. WIINTROBE METHOD
1. WESTERGREN METHOD
In this method westergren tube
is used to determine ESR.
WESTERGREN TUBE
The tube is 300 mm long and
opened on both ends . It is marked 0 to 200 mm from above down ward .
Westergren tube is used only for determining ESR.
1.6 ml of blood is mixed with 0.4 ml of 3.8% sodium citrate and loaded in the westergren tube. The ratio of blood and anticoagulant is 4:1. The tube is fitted to the stand vertically and left undisturbed. The reading is taken at the end of 1 hour.
1.6 ml of blood is mixed with 0.4 ml of 3.8% sodium citrate and loaded in the westergren tube. The ratio of blood and anticoagulant is 4:1. The tube is fitted to the stand vertically and left undisturbed. The reading is taken at the end of 1 hour.
WINTROBE METHOD
Wintrobe Tube
Wintrobe Tube is a short tube
opened on only one end. It is 110 mm long with 3 mm bore. Wintrobe
tube is used for determining ESR and PCV. It is marked on both sides.
NORMAL VALUE OF ESR
By westergren Method
In
males : 3 to 7 mm in 1
hour
In females : 5 to 9 mm in 1 hour
Infants : 0 to 2 mm in 1 hour
In females : 5 to 9 mm in 1 hour
Infants : 0 to 2 mm in 1 hour
By wintrobe method
In
males : 0 to 9 mm in 1 hour
In females : 0 to 15 mm in 1 hour
Infants : 0 to 5 mm in 1 hour
In females : 0 to 15 mm in 1 hour
Infants : 0 to 5 mm in 1 hour
VARIATIONS OF ESR
Physiological Variation
1. Age
ESR is less in Chhidren and
infant because of more number of RBCs
2. Sex
It is more in females than in
males because of less number of RBCs.
3. Menstruration
The ESR increases during
menstruation because of loss of blood and RBCs.
4. Pregnancy
From 3rd month to parturation
ESR increases up to 35 mm in 1 hour because of hemodilution.
 |
| WESTERGREN TUBE |
PATHOLOGICAL VARIATIONS
1. Tberculosis
2. All types of anemia except
sickle cell anemia
3. Malignant tumors
4. Rheumatoid arthritis
5. Rheumatic fever
6. Liver diseases.
FACTORS AFFECTING ESR
Factor increaseng ESR
1. Specific Gravity of RBC
2. Rouleaux Formation
3. Increase in Size of RBC
Factors Decreasing ESR
1. Viscosity of blood
2. RBC count
PACKED CELL VOLUME AND BLOOD
INDICES
Definition
Packed cell volume is the
propartion of blood occupied by RBCs expressed in percentage. It is the volume
of RBCs packed at the bottom of a hematocrit tube when the blood is
centrifuged. It is also called hematocrit value or erythrocyte volume fraction
(EVF).
NORMAL VALUES OF PCV
Normal
In
males = 40% to 45%
In females = 38% to 42%
In females = 38% to 42%
VARIATIONS IN PCV
Increase in PCV
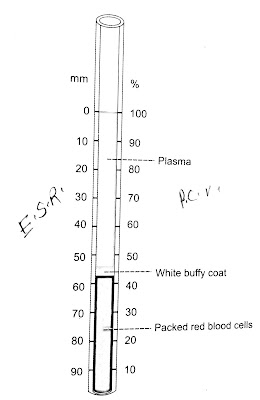 |
| PACKED CELL VOLUME |
1. Polycythemia
2. Dehydration
3. Dengue shock syndrome
2. Dehydration
3. Dengue shock syndrome
Decrease in PCV
1. Anemia
2. Cirrhosis of liver
3. Pregnancy
2. Cirrhosis of liver
3. Pregnancy

0 comments:
Post a Comment